
news
2023.2.27
Centrifugal casting is a casting method in which molten metal is poured into a high-speed rotating metal mold. Under the action of centrifugal casting machine, the mold rotates at a high speed and is driven by its centrifugal force to cool and crystallize. Here is everything you should know about centrifugal casting.
Metals that are molten can be shaped through the process of casting. There is a wide variety of casting processes available. Sand casting frequently employs the usage of Z. There have been a number of new and increased demands placed on casting technology as a result of the increasing sophistication of modern industrial technology and the widespread social necessity for its application. It consists primarily of the following three elements:
1. In addition to boosting output, manufacturers must work to enhance casting quality in a number of ways. These include making castings smoother on the outside and reducing flaws of different kinds.
2. Make an effort to streamline its procedures, boost its productivity, enhance the amount of automation in its modeling, and lessen the strain on its workforce;
3. Decrease production costs by decreasing metal material usage to Z.
In recent years, people have devised many different casting procedures in order to accomplish the aforementioned goals by combining old casting technology with modern scientific and technological advances. Special casting techniques are another name for sand casting that helps to set them apart from the more commonplace approach of using sand. An Overview of the Most Popular Casting Techniques
Casting methods such as
-Lost wax casting
-Metal mold casting
-Low pressure casting
-Centrifugal casting
-Ceramic mold casting
-Pressure casting
-Lost foam casting
-Magnetic mold casting
Special casting differs greatly from conventional sand casting in the materials, processes, and molds that are employed.
It wasn’t until the turn of the past century that centrifugal casting began to be widely used in industrial production, despite the fact that it had been around for 70 or 80 years since its development. China didn’t start making cast iron pipes with centrifugal casting until the 1940s.
Nowadays, centrifugal casting is one of the most popular techniques for making castings like disk rings and pipe sleeves.
Impellers, paper producing blanks, seamless pipe blanks, bimetallic castings (such steel sleeve copper bearing rollers, etc.), and so on can all be made with centrifugal casting. These days, centrifugal casting machines are highly automated and mechanical. The annual production of some mechanized centrifugal pipe casting factories is over 100,000 tons.
A centrifugal casting machine is used to rotate the mold during the casting process. According to the orientation of the mold rotation space, centrifugal casting machines can be classified as either vertical or horizontal.
The mold in a centrifugal casting machine revolves vertically. Castings have a thin top and thick bottom because of centrifugal force and the gravity of the liquid metal itself, which causes the inner surface to be parabolic in form. Assuming all else is constant, the greater the casting height, the greater the wall thickness difference. Because of the unequal wall thickness under the gravity of the liquid metal itself, the subsequent cutting process needs to be enhanced, making vertical centrifugal casting primarily useful for castings of disks and rings with diameters smaller than the diameter.
Casting machine in which the mold spins horizontally, using centrifugal force. It is possible to cast uniformly thick-walled cylinders and pipe sleeves because the cooling conditions over the whole casting are consistent.
Centrifugal casting provides the following features because liquid metal fills the mold and hardens while the mold is rotated:
The feeding environment is improved because the centrifugal part of the casting makes the other parts fine and dense by tossing the metal liquid from the mold wall to the inner surface of the casting, with a certain directional cooling crystallization. The mechanical qualities of castings are enhanced by the application of pressure, which also helps to seal shrinkage and other casting faults.
Second, a runner or casting riser is unnecessary for centrifugal casting. It is possible to eliminate the core while casting hollow castings, increasing metal consumption to 80-90 percent while decreasing production costs and enhancing productivity.
Third, Z can be used to make hollow castings. Traditional sand casting requires more time and effort to disassemble and reassemble movable cores, consumes more raw materials, and requires more workers to get the job done.
The number of alloys that can be used in centrifugal casting is practically infinite.
Casting machine specifications
Specifically, a vertical centrifugal casting machine with a 75 kW motor, a 600 rpm spindle high speed, and a stepless speed regulator is used. The equipment has a 1100 mm Z major diameter casting, an 1800 mm Z major height, and a 15 t Z major bearing mass (casting+mold).
Modeling a Mold
Centrifugal casting molds typically have a metal mold barrel, baffle, and bottom plate sandwiching a sand core. It is not necessary to consider the draft angle of the casting because most of the inner and outer circles of the conical section drum are conical, the straight section part is short, and the casting scale is usually about 2%. This is in addition to the chilling effect of the metal mold barrel on the casting, which allows for easy demolding after cooling shrinkage. This is a picture of the mold layout for better vertical centrifugal casting.
-Metal cylinder composition analysis:
In order to prevent defects in the metal outer mold from being caused by the local temperature of the metal outer mold rising above its transformation temperature Ac1 (the transformation temperature at the beginning of austenitizing), 30CrMo, 34CrMo, and 21CrMo10 are the materials of choice for centrifugal casting metal mold barrels both domestically and internationally.
The high alloy content of 21CrMo10 material, the temperature of Ac1 is 768 °C, and the toughness is good, which has the characteristics of preventing the formation of hot cracks, makes it the material of choice for the metal cylinder due to the high production volume of the cone section drum and the need to ensure the long service life of the metal outer mold.
-Measurement of the metal cylinder mold’s wall thickness:
In horizontal centrifugal casting, the heat of casting is typically passed to the metal mold barrel because the contact area between the baffle and the casting is typically considerably smaller than that of the metal mold barrel. Metal mold barrel wall thickness in horizontal centrifugal casting is determined by the following factors: Mold and casting wall thickness Casting ratio Type/ It can be cast between 1.4 and 2.0.
Though the sand core in an enhanced vertical centrifugal casting is placed on the metal mold’s base plate, it nevertheless absorbs a great deal of heat from the casting and releases a great deal of water vapor as a byproduct of this process. Discharging the heat through the bottom plate causes the water vapor to remove most of it, thus the bottom plate and baffle only need to absorb a fraction of the heat that the metal mold cylinder does. Hence, the horizontal centrifugal casting can be used as a reference when calculating the wall thickness of the metal mold barrel for the enhanced vertical centrifugal casting.
The mold thickness ranges from 71.4 to 102.0 millimeters, and the primary wall thickness Z of the enhanced conical section drum casting is 51 millimeters. To account for the fact that the wall thickness of the conical drum casting has increased in some areas, the wall thickness of the metal mold barrel is calculated to be 90mm Type/ Cast=1.7.
Pre-use mold interior treatment
After being machined, the metal mold cylinder’s working surface is quite smooth and clean, albeit there is oil staining and other signs of previous use. After spraying, the coating frequently peels off, leading to flaws like slag inclusion in the casting. Hence, after spraying the mold barrel with paint for the first time, it is customary to clean it with the metal liquid at the proper temperature before using it again.
Production experience has shown that the working surface of the metal mold barrel is best prepared for its first use by adding a small amount of salt to the sprayed coating in advance and then applying it. After 5 to 7 days of storage, the coating is removed and the metal mold barrel is ready for use after being cleaned with fresh water.
Mold machining allowance determination
While using centrifugal casting, the molten metal is supplied in while being spun at high speeds. In most cases, flaws like porosity and slag inclusions are absent. Since the inner surface and the two end faces of the conical drum casting are where the majority of the impurities are found, they have a larger machining allowance than the outer surface.
It is unnecessary to account for the effect of shrinkage on the wall thickness of the casting when calculating the machining allowance, as this was prevented in the modernized vertical centrifugal casting process by the use of sand cores.
So, the one-sided machining allowance is as follows: 20mm for the small diameter end of the cone section drum, 16mm for the large diameter end of the cone section drum, 6mm for the outside circle of the cone section drum, and 10mm for the inner hole of the cone section drum.
Determining the RPM of the Mold Rotation
Constantinov formula is used to calculate the casting speed:
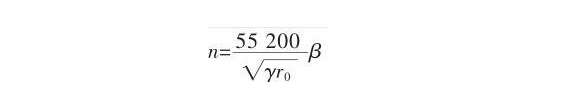
Casting speed, in revolutions per minute, is denoted by n;
—— Density of liquid alloy, in N/m3;
R0 = casting’s inner radius (in meters);
A vertical centrifugal casting process for steel requires an adjustment factor of 1.0–1.3.
UNSJ93371 duplex stainless steel, = 7.8 104N/m3, is used for the huge stainless steel cone drum of an imported centrifugal separator. It is possible to choose r0 according to the straight section, that is, r0=137.5mm, because of the sand core added to the cone section. The aforesaid formula allows us to determine that the necessary centrifugal speed for the mold is 533.0692.9 r/min.
At this point, the mold’s centrifugal speed, n, is 560 revolutions per minute (= 1.05 seconds).
Coating of metal mold barrel
Coating the metal mold cylinder with a consistent and flat 1.2–1.5mm thick silica powder water-based coating is required. Coating of the metal mold barrel and sand core must occur after preheating; further heating is not required after spraying.The ideal heating time for the mold’s metal barrel and sand core
The metal cylinder needs to be preheated to a temperature between 180 and 240 degrees Celsius. Coating spraying requires preheating to between 180 and 240 degrees Fahrenheit (between 160 and 120 degrees Celsius). Once coated, it can be used as a pouring vessel.
Resin sand is used for the core, and preheating occurs between 120 and 150 degrees Celsius for no more than an hour so that the sand doesn’t become too brittle and fall apart while pouring; the water vapor that’s trapped in the sand is what carries the heat out of the bottom plate hole. The coating needs to be sprayed after being heated, and then it can be poured.
The Pouring Temperature is Determined
The melting point of duplex stainless steel is close to 1440 degrees Celsius. The enhanced vertical centrifugal casting method is used, with a pouring temperature of around 120–230 °C above the melting point (1560–1670 °C). Pouring at 1580-1600 °C ensures that all of the gas trapped in the mold cavity is released without damaging the mold, although this high temperature is not ideal for mold protection.
Finding the demoulding temperature for a casting
Centrifugal force is used to fill the casting, which then hardens. At temperatures below roughly 700 degrees Celsius, centrifugal force is negligible. In order to safeguard the vertical centrifuge, the casting can be lifted at any time during the process and removed. The casting must be allowed to cool naturally to a temperature of around 300 degrees Celsius before being demoulded.
