A mold or mould are the common terms used to describe the tool used in the manufacturing process, both die casting and injection molding use the molds to create parts. Then, how do they work and what’s the difference between die casting mold and plastic injection mold?
What is Die Casting Mold?
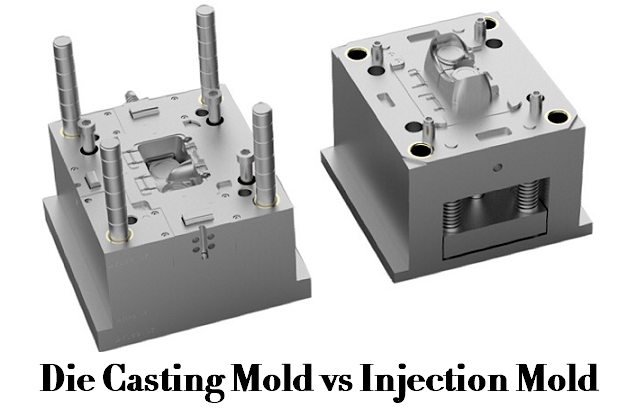
Die casting mold, also known as the die or tool used in the die casting process, contains the mold cavity which is created using two hardened tool steel dies and used to form the contours and dimensions of the casting. A die casting mold is made of two parts and consists of fixed and movable mold shelves. The fixed half die is installed on the fixed plate of the die casting machine; The ejector half die is fixed on the movable fixed plate, including the casting ejector.
What is Plastic Injection Mold?
Plastic injection mold refers to the tooling used to produce plastic parts in the injection molding process, it is typically constructed from hardened steel, aluminum, and other alloys. An injection mold is composed of a series of parts that allows molten plastic to be cooled and form the desired shape. Steel molds are usually more expensive to build, but have a longer service life, which will offset the higher initial cost compared to the greater number of parts manufactured before wear.
What is Die Mold?
A die mold is a specialized tool used in manufacturing to shape molten metal, plastic, or other materials into a specific form by using a cavity inside the mold. It’s made of hardened steel or aluminum and designed to withstand high pressure and temperature during the casting or molding process. In die casting, molten metal (like aluminum or zinc) is injected into the mold die cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape—such as automotive parts, electronic housings, or decorative items. The die mold ensures high precision, repeatability, and smooth surface finishes, making it a critical component in mass production of detailed and durable parts.
Die Molding Process
Die molding, also called die casting or molding, is a manufacturing process where molten material—usually metal (like zinc, aluminum, or magnesium) or plastic—is forced into a precision-engineered mold cavity under high pressure. Here’s a step-by-step overview:
Mold Preparation:
The die (mold) is cleaned, preheated (for metals), and coated with a lubricant or release agent to prevent sticking.
Melting the Material:
The chosen material is heated until it reaches a fully molten state.
Injection into the Mold:
The molten material is injected or pressed into the die cavity using high pressure to ensure it fills every detail.
Cooling and Solidification:
The material quickly cools and solidifies in the shape of the mold cavity, forming a precise and detailed part.
Ejection:
Once solidified, the part is ejected from the mold using pins or mechanical ejectors.
Trimming and Finishing:
Excess material (flash) is removed, and surface finishing, painting, or machining may be done as needed.
Advantages of Mold Die
1. High Precision: Mold dies produce parts with excellent dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes.
2. Mass Production Efficiency: Once created, a mold die can produce thousands of identical parts quickly, ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
3. Material Versatility: Suitable for metals, plastics, and composite materials, depending on the process (die casting or injection molding).
4. Reduced Waste: The process is highly efficient, minimizing excess material and lowering production costs.
5. Strong and Durable Parts: Mold die processes, especially die casting, result in dense and durable components that withstand wear and stress.
6. Complex Shapes Possible: Enables production of intricate geometries that would be difficult or costly to machine manually.
7. Consistent Quality: Every cycle produces uniform parts, ensuring consistent quality across production batches.
Mould Die Applications
Automotive Industry:
Used to produce engine parts, transmission housings, wheels, and body components with high strength and precision.
Electronics:
Essential for manufacturing heat sinks, mobile casings, connectors, and other small detailed components.
Aerospace:
Creates lightweight yet durable parts such as brackets, housings, and airframe components.
Consumer Goods:
Used for making metal and plastic products like kitchenware, toys, tools, and appliance parts.
Medical Devices:
Produces precise and hygienic parts for surgical instruments, implants, and equipment housings.
Construction Industry:
Helps manufacture components such as window frames, handles, and fixtures with uniform quality.
Industrial Machinery:
Forms parts like gears, pumps, and motor housings that require tight tolerances and durability.
Difference Between Die Mold and Plastic Injection Mold
The structure of die casting mold is similar to that of plastic mold. The main difference between die casting mold and plastic mold is that on the feed gate sleeve, the gate sleeve of the plastic mold is a slender taper, and the diameter of the inlet is relatively small; while the inlet of the die casting die is relatively large.
1. The injection pressure of the die casting mold is large, so the die is required to be relatively thicker to prevent deformation
2. The gate of the die casting mold is different from that of injection mold, so a shunt cone is needed to decompose the high pressure of the material flow.
3. The core of the die casting die does not need quenching, while the general injection mold should be quenched above HRC52.
4. Generally, the die-casting die cavity shall be nitrided to prevent the alloy from sticking to the die cavity.
5. Generally, the corrosion of the die casting die is relatively large.
6. Compared with the injection mold, the clearance of the movable fitting part of the die-casting mold (such as core pulling slider) is larger, because the high temperature in the die casting process will cause thermal expansion. If the gap is too small, the die will be stuck.
7. The parting surface matching requirements of die casting die are higher, because the fluidity of alloy is much better than that of plastic. It is very dangerous for high temperature and high pressure material flow to fly out of the parting surface.
8. Generally, the injection mold can be vented by a parting surface. The die mold must be provided with an exhaust slot and slag collection bag.
9. Die casting mold injects faster, plastic injection is divided into several stages.
10. The die casting mold consists of two halves. The product structure of different plastic molds is different.
11. Plastic molds and mould dies are made of different steels. Plastic molds generally use 45# steel, T8, T10, and other steel, while die-casting molds mainly use heat-resistant steel such as 3Cr2W8V.
| Feature | Die Mold | Plastic Injection Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Material Used | Metals (zinc, aluminum, magnesium) | Thermoplastics (ABS, PP, PVC, Nylon) |
| Process | Die casting – molten metal is injected under high pressure | Injection molding – molten plastic is injected into mold cavity |
| Production Speed | Fast for metals, but slower than plastic for very high volumes | Very fast, ideal for mass production |
| Precision | High, especially for detailed metal parts | High, but depends on plastic shrinkage |
| Cost of Mold | Expensive due to metal and machining | Generally lower than metal molds, depends on complexity |
| Product Strength | Very strong, durable, and heat-resistant | Less strong than metals, suitable for lightweight parts |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, hardware, metal toys, machinery components | Plastic containers, consumer products, electronics housings |
| Cooling Time | Metal cools slower than plastic; requires longer cycle | Plastic cools quickly; shorter cycle times |
| Weight of Finished Product | Heavy, solid | Light, can be hollow if designed with cores |
| Post-Processing | Often requires trimming, finishing, or machining | Minimal; may require trimming, polishing, or painting |

