Hot chamber die casting is an efficient manufacturing process that produces high-precision and high-quality parts by melting and injecting metal into a mold. The die-casting process is widely used in the automotive, electronics, aerospace, medical and other industries.
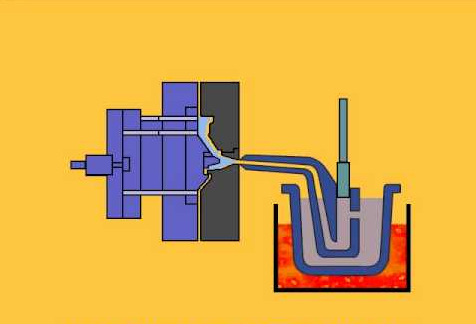
Components of Hot Chamber Die Casting
The components of a hot chamber die casting machine vary by model and manufacturer, but generally include the following components:
-Furnace: The furnace is one of the core components of the hot chamber die casting machine, which is used to heat the metal to a molten state for injection into the mold.
-Burner: The burner is the component of the furnace responsible for providing the gas and air mixture required for combustion.
-Hot chamber: The hot chamber is a vessel, connected between the furnace and the injection system, responsible for keeping the molten metal at the right temperature and pressure for injection into the mould.
-Casting system: The casting system includes injection cylinder, plunger/piston, nozzle, gooseneck and other components, which are responsible for injecting molten metal from the hot chamber into the mold.
-Mould: The mold is the key part of manufacturing parts, which is composed of upper mold and lower mold. The hot chamber die casting machine injects molten metal into the mold and solidifies it into the required parts in the mold.
-Ejector pin: Ejector pin is a component of the mold used to release the part from the mold.
Suitable & Unsuitable Materials for Hot Chamber Die Casting
The hot chamber die-casting process is suitable for the manufacture of high melting point metals and alloys. Different materials have different characteristics and application scenarios, which need to be selected according to specific conditions.
The following is a comparative analysis of data about materials suitable and unsuitable for hot chamber die casting, and a table is given for summary:
| Material | Melting Point (°C) | Thermal Conductivity(W/(m·K)) | Oxidation & Porosity Issues | Is it suitable for hot chamber die casting |
| Aluminum Alloy | 660 | 200 | Easy to produce pores | Not suitable |
| Zinc Alloy | 419 | 120 | Less oxidizing, fewer porosity issues | Suitable |
| Copper Alloy | 1000 | 400 | Less oxidizing, fewer porosity issues | Suitable |
| Magnesium Alloy | 650 | 156 | Less oxidizing, fewer porosity issues | Suitable |
| Lead Alloy | 327 | 35 | Less oxidizing, fewer porosity issues | Suitable |
Hot Chamber Die Casting Process
Different hot chamber die casting machines and different component manufacturing processes may have some subtle differences, so the following is a summary table of parameter standards for different materials and product requirements of the hot chamber die casting process. In practical application, it should be adjusted and optimized according to the specific situation.
| Step | Parameter | Aluminum Alloy | Zinc Alloy | Copper Alloy | Magnesium Alloy | Lead Alloy |
| Prepare the mold | Mold Material | High strength, high temperature resistance | High strength, high temperature resistance | High strength, high temperature resistance | High strength, high temperature resistance | High strength, high temperature resistance |
| Die Geometry & Shape | Meet the design requirements | Meet the design requirements | Meet the design requirements | Meet the design requirements | Meet the design requirements | |
| Die surface finish and lubricity | High finish, good lubrication | High finish, good lubrication | High finish, good lubrication | High finish, good lubrication | High finish, good lubrication | |
| Heating Metal | Heating Temperature | 670-710°C | 380-420°C | 960-1000°C | 610-650°C | 310-327°C |
| Heating rate | Fast | Fast | Fast | Fast | Fast | |
| Heating Time | Short | Short | Short | Short | 短Short | |
| Injection Mold | Injection Speed/Pressure/Time | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Cooling Parts | Cooling Time | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Cooling Method & Medium | Uniform, Water | Uniform, Water | Uniform, Water | Uniform, Water | Uniform, Water | |
| Take Out Parts | Size and Shape | Meet the Requirements | Meet the Requirements | Meet the Requirements | Meet the Requirements | Meet the Requirements |
| Lubricating Properties | Good | Good | Good | Good | Good |
Applications of Hot Chamber Die Casting
Hot chamber die casting is used in a wide variety of applications, especially in industries such as automotive manufacturing, electronics, aerospace and medical devices. And it has brought high-quality, high-precision and high-efficiency manufacturing solutions to various industries. The following are a few examples of hot chamber die casting applications in various industries:
1. Automotive industry
Hot chamber die casting is widely used in the automotive industry, especially in the manufacture of critical components such as engines and transmissions. For example, Mercedes-Benz uses a hot chamber die-casting process to manufacture engine blocks and cylinder heads to improve product quality and production efficiency. In addition, Ford also uses hot chamber die-casting technology to manufacture parts such as engine blocks and transmission gears.
2. Electronic industry
In the electronics industry, especially in the manufacture of components such as electronic housings and heat sinks. Hot chamber die-casting has been widely used. For example, Apple’s MacBook Pro notebook computer uses a hot-chamber die-cast aluminum alloy shell to improve the appearance and heat dissipation performance of the product.
3. Aerospace industry
Hot chamber die casting is used in the aerospace industry, especially in the manufacture of aircraft engines and aerospace components. For example, General Electric uses the hot chamber die casting process to manufacture key components such as the high-pressure and low-pressure turbines in the LEAP engine.
4. Medical industry
Hot chamber die casting is also widely used in the medical device industry, especially in the manufacture of components such as artificial joints and dental implants. For example, Hermann Berlin, Germany has manufactured artificial joint parts using hot chamber die-casting technology, and has ensured the high precision and high quality of the products through strict quality control.
What Is the Difference between Hot Chamber Die Casting and Cold Chamber Die Casting
There are many differences between hot chamber die casting and cold chamber die casting. The advantage of hot chamber die casting is that it can manufacture high-precision, high-quality parts, and high production efficiency, but the equipment cost and mold costs are relatively expensive, and it is suitable for the manufacture of high melting point metals. The advantage of cold chamber die casting is that the equipment cost and mold cost are low, and it is suitable for the manufacture of low melting point metals, but the precision is low, and it is not suitable for the manufacture of complex parts. Therefore, the specific choice of hot chamber die-casting or cold chamber die-casting should be determined according to the specific situation.
| Point of Difference | Hot Chamber Die Casting | Cold Chamber Die Casting |
| Molten Metal | in a hot chamber | in an external furnace |
| Melting Temperature | Higher | Lower |
| Metal Fluidity | Better | Poor |
| Precision | Higher | Lower |
| Productivity | High | Low |
| Applicable Material | High Melting Point Metal | Low Melting Point Metal |
| Equipment Cost | Expensive | Cheaper |
| Mold Cost | Low | High |
| Manufacturing Complex Parts | Be Applicable | Not applicable |

