Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer made from the monomer ethylene. Since its invention in the 1930s, LDPE has become an integral material in various industries due to its unique properties such as flexibility, toughness, and chemical resistance. This article delves into the characteristics of LDPE, its production process, applications, and the environmental considerations associated with its use.
Properties of LDPE
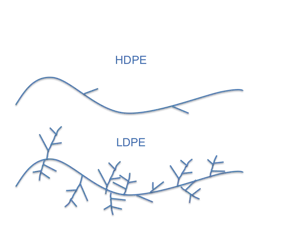
LDPE is a semi-rigid and translucent polymer. Its low density (0.910–0.925 g/cm³) is a result of its highly branched polymer chain structure, which prevents the chains from packing closely in a crystalline arrangement, resulting in a less dense material compared to High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE).
| Property | Value |
| Density | 0.92-0.94 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 105-115 °C (220-240°F) |
| Tensile strength | 14-21 MPa (2,000-3,000 psi) |
| Elongation at break | 300-600% |
| Young’s modulus | 150-300 MPa (20,000-40,000 psi) |
| Impact strength | 200-500 J/m (150-360 ft-lbf/in) |
| Hardness | Shore D 50-60 |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.35-0.5 W/(m·K) (0.2-0.3 Btu·in)/(ft2·h·°F) |
| Heat deflection temperature | 55-75 °C (130-165 °F) at 0.45 MPa (64.7 psi) |
| Vicat softening temperature | 90-100 °C (194-212 °F) |
| Material property class | Thermoplastic |
| Chemical resistance | Fair to good (resistant to water, alcohols, dilute acids and bases) |
| Electrical resistivity | 1016 Ω·cm |
Production of LDPE
The production of LDPE typically involves a high-pressure polymerization process. Here’s an overview of the production stages:
- 1. Ethylene Production
Ethylene is primarily produced through the steam cracking of hydrocarbons. Naphtha, natural gas liquids, and other petroleum products are heated to high temperatures to break down larger molecules into ethylene and other byproducts.
- 2. Polymerization
Ethylene gas is subjected to high pressure (up to 300 MPa) and temperatures (80 to 300 °C) in a reactor in the presence of an initiator, which causes the ethylene molecules to react and form the polyethylene chains. The high-pressure process is what gives LDPE its characteristic branching.
- 3. Extrusion and Pelletizing
The molten polymer is then extruded through a die to create thin strands of LDPE, which are cooled and cut into granules or pellets. These pellets are the raw material for various molding and extrusion processes used to manufacture end products.
Applications of LDPE
LDPE’s versatility makes it suitable for a broad range of applications. The following are some common uses:
1. Packaging
- -Food Packaging: LDPE is used to produce cling films, bags for bread, frozen foods, and snacks. Its moisture resistance helps prolong the shelf life of food products.
- -Bottles and Containers: While not as rigid as HDPE, LDPE is used to make squeeze bottles and containers for food and non-food items.
- -Agricultural Films: LDPE films are used in agriculture for soil moisture retention and weed control.
2. Consumer Goods
- -Toys: The safety and flexibility of LDPE make it ideal for children’s toys.
- -Housewares: LDPE is used in kitchenware, trash bins, and various household items for its durability and chemical resistance.
3. Construction
- -Pipes and Fittings: LDPE is used in water piping systems due to its low water absorption and chemical resistance.
- -Insulation: The insulating properties of LDPE make it a material of choice for cable and wire insulation.
4. Medical
Medical Devices: LDPE’s non-reactivity makes it suitable for manufacturing certain medical devices and containers.
Environmental Considerations
The widespread use of LDPE has raised environmental concerns, particularly related to waste management and pollution. LDPE is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for a long time. Recycling LDPE can mitigate some of these issues, but the recycling rates for LDPE are generally lower than for other plastics due to collection and processing challenges.
Efforts to improve the sustainability of LDPE include:
- -Advancing Recycling Technologies: Improving mechanical and chemical recycling methods to increase the recyclability of LDPE.
- -Developing Biodegradable Alternatives: Research into biodegradable polymers aims at reducing the environmental impact of plastic products.
- -Promoting Circular Economy: Encouraging the design of products for reuse and recycling to minimize waste.
Low-density polyethylene is a ubiquitous material with a multitude of applications ranging from packaging to consumer goods. Its unique combination of flexibility, moisture resistance, and chemical stability has cemented its role in modern manufacturing. However, the environmental impact of LDPE necessitates a continued focus on recycling, waste reduction, and the development of eco-friendly alternatives. As we navigate towards a more sustainable future, the role of LDPE and similar polymers will continue to evolve, balancing the demands of industry with the imperative of environmental stewardship.

