Slag inclusion defects can be problematic and can compromise the strength and integrity of the casting. It is important to identify and address slag inclusion issues and prevent them to improve the casting quality.
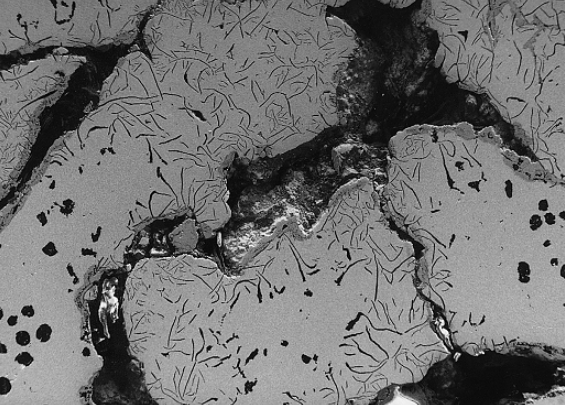
What Is Slag Inclusion in Casting?
Slag inclusion is a type of defect that can occur in casting. Slag is a byproduct of the metal casting process, and it consists of impurities and non-metallic materials that can become trapped in the casting. When slag is present in the casting, it can weaken the structure and reduce the overall quality of the final product. Slag inclusion often occurs when the slag is not properly removed from the mold or when it is introduced into the casting process through other means, such as a contaminated casting material. The presence of slag can cause a variety of problems in the casting, including reduced mechanical strength, reduced ductility, and reduced resistance to corrosion.
What Causes Slag Inclusion in Casting?
Slag inclusion in casting can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
– Improper cleaning of the mold: If the mold is not properly cleaned or prepared before casting, it can contain contaminants such as rust, dirt, or sand, which can become trapped in the casting and cause slag inclusion.
– Contaminated casting material: The use of contaminated casting material, such as scrap metal or alloys with a high content of impurities, can introduce slag into the casting.
– Poor gating and riser design: Improper gating and riser design can cause turbulence in the molten metal, leading to the entrapment of slag in the casting.
– Incorrect pouring temperature: If the pouring temperature is too low, the molten metal may not be able to fill the mold completely, causing slag to be trapped in the voids.
– Inadequate venting: If the mold is not properly vented, gases may become trapped in the casting, which can cause slag inclusion.
– Lack of proper inspection and testing: Without proper inspection and testing, it can be difficult to identify and address slag inclusion issues before they become more serious.
Is slag inclusion external or internal? Slag inclusion can be both internal and external, depending on where the slag is trapped in the casting. Internal slag inclusion occurs when the slag becomes trapped within the metal casting and is not visible on the surface of the casting. This can occur when the slag becomes trapped within the molten metal as it cools and solidifies, or if the slag is introduced into the casting through impure materials or inadequate cleaning of the mold. External slag inclusion, on the other hand, occurs when the slag becomes trapped on the surface of the casting. This can happen when the slag is not properly removed from the mold or if it is introduced onto the surface of the casting during the casting process.
How Do You Prevent Slag Inclusions?
Slag inclusion in casting can be prevented by following proper casting procedures and taking necessary precautions throughout the process. Here are some steps that can help to prevent slag inclusion:
– Use high-quality materials: Ensure that the casting material is of high quality and does not contain impurities or contaminants that could lead to slag inclusion.
– Properly clean the mold: The mold should be properly cleaned and prepared before casting to ensure that no contaminants are present.
– Use adequate gating and riser design: Proper gating and riser design can prevent turbulence in the molten metal and minimize the risk of slag inclusion.
– Control pouring temperature: The pouring temperature should be controlled to ensure that the molten metal can fill the mold completely and minimize the risk of slag entrapment.
– Adequate venting: Proper venting can prevent the entrapment of gases in the casting, which can cause slag inclusion.
– Inspect and test the casting: Regular inspection and testing can help to identify and address any issues with slag inclusion before they become more serious.
– Use suitable casting techniques: The casting techniques used should be suitable for the type of metal and the desired outcome, with proper attention to mold design, cooling rate, and other factors.

