Aluminum is a popular material for extrusion and shaping profiles due to its excellent mechanical properties and versatility. Its high ductility allows it to be easily shaped, while its lower melting point compared to steel makes the processing more energy-efficient. Additionally, aluminum has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for industrial applications where both strength and lightweight characteristics are required.
When it comes to aluminum profiles, designations like 6061-T4, 6061-T6, 6063-T5, or 6063-T6 refer to both the grade of aluminum and the tempering process it has undergone. The temper (T4, T5, T6) indicates the heat treatment process, which significantly affects the material’s mechanical properties and suitability for specific applications. Here we will explain the differences between T4, T5, and T6 temper aluminum and help you decide which one is best suited for your project.
What is T4 Temper Aluminum?
T4 aluminum has undergone solution heat treatment followed by natural aging. In this state, the material is cooled after extrusion but does not undergo artificial aging in a furnace. As a result, T4 aluminum has relatively lower hardness but better deformability, making it suitable for applications that require subsequent bending or forming.
T4 Heat Treatment Process
T4 heat treatment is an important tempering process in the processing of aluminum alloy materials. It mainly includes two steps:
- Step 1 – Solution treatment: The aluminum alloy material is heated to a high temperature single-phase region (usually between 460-490℃) and maintained for a period of time (generally 1-2 hours) to ensure that the alloying elements are fully dissolved into the aluminum matrix. It is then rapidly cooled, usually by water quenching or air quenching, to prevent grain growth and maintain a fine grain structure.
- Step 2 – Natural aging: The solution-treated aluminum alloy material is placed at room temperature to allow the second phase particles in the alloy to slowly precipitate. The time of this stage depends on the thickness of the material. Generally, thinner materials take a few days, while thicker parts may take a few weeks. During the natural aging process, the properties of the material will gradually stabilize and reach the required mechanical properties.
Through this treatment, the strength and toughness of aluminum alloys can be significantly improved, making them have a wider application prospect in aerospace, transportation, and construction. Compared with T6 heat treatment, T4 heat treatment has a simpler operation process and less energy consumption, so it is more advantageous in certain application scenarios.
Properties of T4 Aluminum:
- Yield Strength: Approximately 110 MPa
- Tensile Strength: Approximately 240 MPa
- Hardness: Lower hardness, around HB 60-70
- Deformability: High, suitable for bending, forming, and other deformation processes
- Corrosion Resistance: Good
Applications of T4 Aluminum:
Ideal for products that need further shaping or deformation, such as automotive body panels or aerospace parts that require flexibility.

What is T5 Temper Aluminum?
T5 aluminum undergoes solution treatment followed by incomplete artificial aging. After extrusion, the aluminum is air-cooled and then transferred to an aging furnace for a few hours at around 200°C. This process increases the material’s hardness while maintaining some degree of deformability. T5 aluminum is commonly used in applications where moderate strength is required, such as architectural profiles.
T5 Heat Treatment Process
Aluminum alloy T5 heat treatment is a commonly used metal processing process. This T5 tempering process mainly includes two key links:
- Step 1 – Quenching treatment: This is the first step of T5 heat treatment. The aluminum alloy is usually heated to a higher temperature (generally above 500℃) and kept for a certain time to ensure that the soluble phase in the alloy is fully dissolved. Subsequently, the aluminum alloy will be quickly quenched into 60-100℃ water to achieve rapid cooling. This process helps to strengthen the dissolution of components in the alloy and fix it to room temperature.
- Step 1 – Aging treatment: This is another key link in T5 heat treatment. Aging treatment is to heat the quenched aluminum alloy to a certain temperature, keep it warm for a certain period of time, and then take it out of the furnace and air cool it to room temperature. This process aims to decompose the supersaturated solid solution and make the alloy matrix structure more stable. The aging treatment in T5 heat treatment is usually incomplete artificial aging, that is, the heating temperature is about 150-170℃ and the holding time is 3-5 hours.
After T5 heat treatment, the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of aluminum alloy are improved, and its strength will be significantly improved. This is because during the heat treatment process, the grains of aluminum alloy are refined and the internal structure is optimized, thereby improving its mechanical properties. Specifically, both tensile strength and yield strength will be improved, and hardness will also increase. Taking AlSi10MgMn aluminum alloy as an example, after T5 heat treatment (especially after 2 hours of insulation at 320℃), its elongation can reach 5.67%, yield strength is 159.67MPa, and tensile strength reaches 262MPa. These data clearly show the positive effect of T5 heat treatment on the strength of aluminum alloy.
Properties of T5 Aluminum:
- Yield Strength: Approximately 160 MPa
- Tensile Strength: Approximately 270 MPa
- Hardness: Moderate hardness, around HB 75-85
- Deformability: Lower than T4, but still allows for some flexibility
- Corrosion Resistance: Moderate to good
Applications of T5 Aluminum:
Suitable for architectural profiles (e.g., windows, doors, curtain walls) and other components requiring a balance of strength and deformability.
What is T6 Temper Aluminum?
T6 aluminum goes through solution treatment followed by complete artificial aging. The aluminum is water-quenched and then aged at a higher temperature for a longer duration. This results in a material with maximum hardness and strength, making it ideal for applications that require high durability and rigidity.
T6 Heat Treatment Process
T6 heat treatment, also known as T6 tempering, mainly involves three core steps:
Step 1 – Solution treatment: Solution treatment is the first step of T6 heat treatment. By heating the material to the single-phase region at a higher temperature, keeping the temperature constant for a period of time, and then cooling rapidly, the stress and excessive hardness inside the material are eliminated to prepare for subsequent treatment. The key to this stage is to control the heating temperature and holding time to ensure that the internal structure of the material is homogenized and to eliminate or reduce the uneven structure and internal stress in the material. During the solution treatment process, the alloying elements in the material will be fully dissolved into the matrix, thereby improving the strength and hardness of the material. In addition, this stage also helps to refine the grains of the material and further improve its comprehensive mechanical properties.
Step 2 – Quenching: Quenching is an important step following the solution treatment. In this stage, the material is brought to an extremely low temperature in a short time by rapid cooling (usually water quenching or oil quenching) to maintain the supersaturated solid solution formed during the solution treatment to prevent precipitation or over-aging. The quenching process is crucial to ensure the effect of the T6 heat treatment. It not only locks in the excellent structure formed in the previous solution treatment stage, but also lays the foundation for the subsequent aging treatment. The success or failure of quenching directly affects the performance of the final material.
Step 3 – Artificial aging: After quenching, artificial aging becomes the last key step of T6 heat treatment. This step is to heat the material to a lower temperature (usually between room temperature and 200 degrees Celsius) for a certain period of time, and then slowly cool it to promote the precipitation of alloy elements in the material and make it more evenly distributed, thereby improving the strength and hardness of the material. During the artificial aging process, the alloy elements are dispersed in the matrix in the form of fine particles, which can effectively hinder the movement of dislocations, thereby improving the strength and hardness of the material. At the same time, aging treatment also helps to further eliminate the internal stress of the material, improve its dimensional stability and corrosion resistance.
The three steps of T6 heat treatment are interrelated and indispensable. Through precise temperature control and time management, T6 heat treatment can significantly improve the strength and hardness of materials such as aluminum alloys, improve their mechanical properties, and meet the needs of various industrial applications, especially in the automotive, aerospace and other engineering fields.
Properties of T6 Aluminum:
- Yield Strength: Approximately 240 MPa
- Tensile Strength: Approximately 310 MPa
- Hardness: High hardness, around HB 90-100
- Deformability: Low, very rigid
- Corrosion Resistance: Good, but slightly lower than T4 due to higher hardness
Applications of T6 Aluminum:
Used in high-strength applications such as aerospace components, automotive parts, and structural applications that demand high tensile strength and rigidity.

T4 vs T5 vs T6 Aluminum: What are the Differences?
The main differences between T4, T5, and T6 aluminum tempers lie in their heat treatment processes, which affect their strength, hardness, and deformability.
| Property | T4 | T5 | T6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Solution treatment + natural aging | Solution treatment + incomplete aging | Solution treatment + full aging |
| Cooling Method | Air-cooled, no artificial aging | Air-cooled, then artificially aged | Water-cooled, then fully artificially aged |
| Yield Strength | ~ 110 MPa | ~ 160 MPa | ~ 240 MPa |
| Tensile Strength | ~ 240 MPa | ~ 270 MPa | ~ 310 MPa |
| Hardness | HB 60-70 | HB 75-85 | HB 90-100 |
| Deformability | High (suitable for bending) | Moderate (some flexibility) | Low (rigid, high hardness) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Moderate to good | Good |
| Applications | Bending, forming, deformable parts | Curtain walls, standard profiles | Aerospace, automotive, structural components |
- T4: Softer and more deformable, suitable for parts that need to be bent or shaped further after extrusion.
- T5: Balanced between strength and flexibility, ideal for architectural applications such as doors, windows, and curtain walls.
- T6: Strongest and most rigid, ideal for high-stress applications like aerospace and automotive parts.
T4 vs T5 vs T6 Aluminum: Which is Better?
The best temper depends on your specific application:
- T4 Aluminum is better for applications requiring bending or additional deformation after extrusion. Its lower hardness allows for more flexibility in shaping.
- T5 Aluminum offers a balance between strength and flexibility, making it ideal for architectural applications where moderate strength and aesthetic finish are important.
- T6 Aluminum provides maximum hardness and strength, making it the best choice for heavy-duty applications like aerospace and automotive components, where high tensile strength and minimal deformability are essential.
The choice between T4, T5, and T6 aluminum tempers depends on the desired mechanical properties for your project. If you prioritize flexibility, go with T4. If you need moderate strength, T5 is a good middle ground. For maximum strength and hardness, T6 is the best choice.
By understanding the differences between these aluminum tempers, you can make an informed decision that ensures your project achieves the right balance of strength, flexibility, and cost.
Mechanical Properties of T1/T4/T5/T6 Aluminum Alloys
To provide a more detailed comparison of the mechanical properties of different aluminum alloys and tempers, the table below outlines the yield strength, tensile strength, elongation, and hardness for various aluminum profiles in the T4, T5, and T6 tempers.
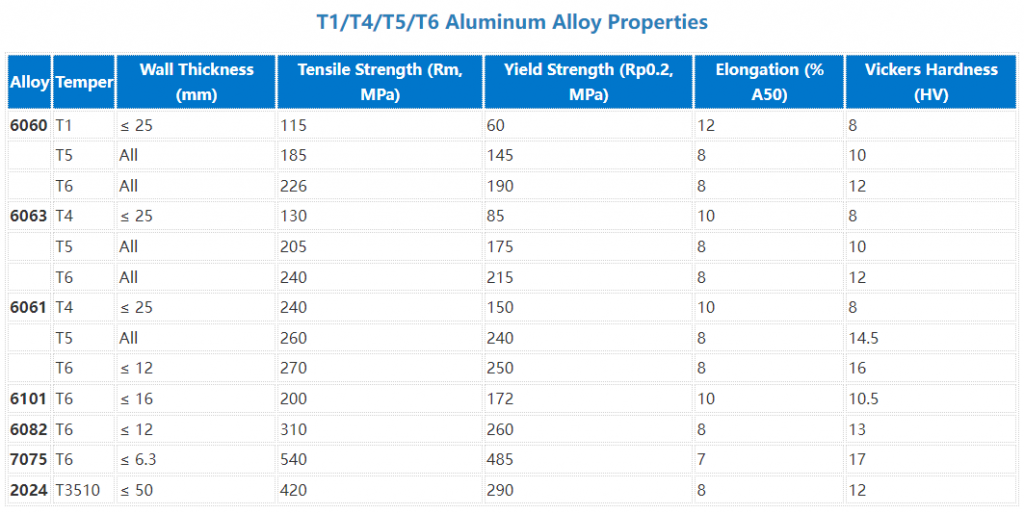
This table highlights the mechanical differences between aluminum profiles in different temper states. For example, 6061-T6 has higher tensile strength and hardness compared to 6063-T6, making it more suitable for applications requiring higher strength, such as in aerospace or automotive components.
Understanding these properties helps in selecting the right aluminum alloy and temper for your specific needs, ensuring the material’s performance aligns with the demands of your project.

