ADC1 aluminum is an alloy that doesn’t always get the spotlight, but its unique properties make it a valuable choice in die casting. With its exceptional fluidity and corrosion resistance, this Al-Si alloy is perfect for thin-walled, complex castings that require precision. While it may not have the highest strength, its lightweight nature and durability make it ideal for automotive frames, electronic housings, and even household appliances. But how does ADC1 compare to the more widely used ADC12? Today, we will take a closer look at ADC1 aluminum composition, properties, applications, and how it stacks up against ADC12, helping you understand where this alloy material excels.

1. What is ADC1 Aluminum Alloy?
ADC1 is an Al-Si aluminum die casting alloy known for its excellent castability and corrosion resistance. It consists primarily of aluminum (Al) and silicon (Si), making it highly fluid in molten form, reducing defects like shrinkage cavities and poor flow.
Due to its low strength, ADC1 is not suitable for applications requiring high mechanical performance. However, it is widely used in automotive components, housing materials, and consumer electronics where corrosion resistance and complex castability are prioritized.
2. ADC1 Aluminum Chemical Composition
The common chemical composition of ADC1 aluminum alloy is:
| Element | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum (Al) | Remainder |
| Silicon (Si) | 11.0 – 13.0 |
| Copper (Cu) | ≤1.0 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | ≤0.3 |
| Zinc (Zn) | ≤0.5 |
| Iron (Fe) | ≤1.3 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤0.3 |
| Nickel (Ni) | ≤0.5 |
| Tin (Sn) | ≤0.1 |
| Lead (Pb) | ≤0.2 |
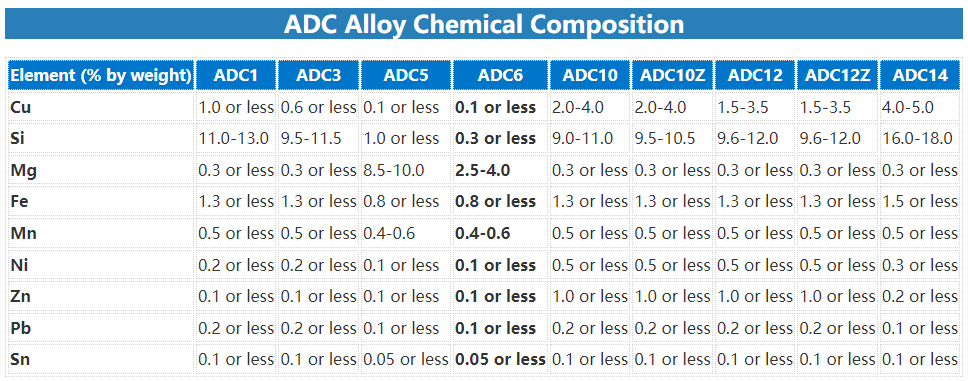
Comparison of Chemical Composition between ADC1 and other ADC Aluminum Alloys
Here we list the following table to show the Chemical Composition of Aluminum Alloys for Die Casting (ADC1, ADC3, ADC5, ADC6, ADC10, ADC12, ADC14), to help you better understand their differences:
3. ADC1 Aluminum Mechanical Properties
ADC1 has relatively low strength but offers good elongation and impact resistance. The key mechanical properties are:
Physical Properties
- Density: ~2.67 g/cm³
- Melting Point: 560 – 580°C
- Thermal Expansion Coefficient: 23.5 × 10⁻⁶/°C (20-100°C)
- Thermal Conductivity: 150 W/(m·K) (20°C)
- Specific Heat Capacity: 897 J/(kg·K) (20°C)
- Electrical Resistivity: 0.035 Ω·mm²/m (20°C)
Mechanical Properties
- Tensile Strength: ≥ 250 MPa
- Yield Strength: ≥ 172 MPa
- Elongation: ≥ 1.7%
- Brinell Hardness: ~71.2
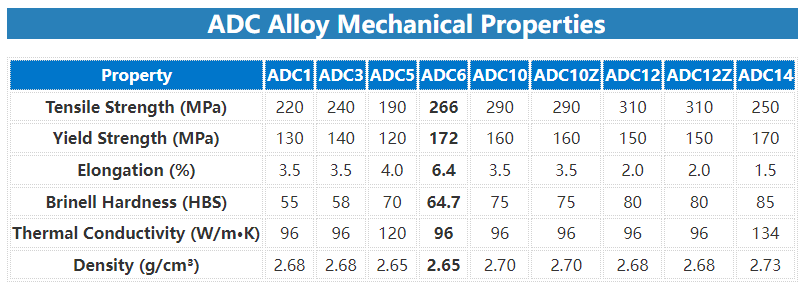
Comparison of Mechanical Properties between ADC1 and other ADC Aluminum Alloys
The mechanical properties of ADC1 compared to other ADC aluminum alloys (ADC3, ADC5, ADC6, ADC10, ADC12, ADC14) is shown below:
ADC1 Aluminum Key Characteristics
1. Excellent Castability
ADC1 is known for its high fluidity, which allows it to fill complex molds with minimal defects. It also has superior casting crack resistance, shrinkage resistance, and melt flow properties compared to other aluminum die casting alloys.
2. High Corrosion Resistance
The aluminum-silicon composition of ADC1 provides good resistance to oxidation and environmental corrosion, making it suitable for applications exposed to moisture and chemicals.
3. Airtightness
ADC1 has one of the highest levels of airtightness among aluminum die casting alloys, making it ideal for applications where leakage prevention is important.
4. Low Strength
While ADC1 is easy to cast, its mechanical strength is relatively low, limiting its use in applications requiring high load-bearing capacity.
ADC 1 Heat Treatment Options
ADC1 can undergo heat treatment to improve its performance:
- Annealing: Conducted at 350-450°C to relieve internal stresses and enhance machinability.
- Solution Treatment: Heating to 450-480°C, followed by rapid cooling to improve strength and toughness.
ADC1 Aluminum Alloy Machining Process
- Casting: Due to its excellent flowability, ADC1 is suitable for thin-walled and intricate castings.
- Cutting: It offers good machinability, allowing for smooth finishing in machining operations.
4. ADC1 Aluminum Equivalent Materials
To ensure interchangeability across global industries, ADC1 Aluminum alloy equivalent materials under different international standards are as follows:
| Standard | Equivalent Material | Notes on Equivalent Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Japan (JIS H5302) | ADC1 | Standard Japanese aluminum die-casting alloy with high silicon content for good castability. |
| USA (AA/ASTM) | A413.0 | High-silicon aluminum alloy with excellent corrosion resistance and good fluidity, often used in automotive and marine applications. |
| Germany (DIN EN 1706) | G-AlSi12 (Cu) (231) | Equivalent to ADC1 in chemical composition and mechanical properties, widely used in die casting applications. |
| United Kingdom (BS 1490) | LM6 | High-silicon aluminum casting alloy with superior corrosion resistance, commonly used in marine and automotive industries. |
| ISO (International Standard) | Al-Si12 | A general-purpose Al-Si casting alloy with good wear resistance and high castability, used in die casting and sand casting. |
| France (NF A57-702) | A-S12 | Similar to ADC1, offering high castability and corrosion resistance, commonly used in automotive and industrial components. |
| Italy (UNI 5079) | AlSi12 | An Al-Si casting alloy equivalent to ADC1, often used in lightweight structural applications. |
| China (GB/T 15115) | YL102 | The Chinese equivalent of ADC1, used in automotive, electrical, and heat dissipation applications. |
5. ADC1 Material Applications (Uses)
ADC1 is commonly used in automotive, electrical, and structural applications where corrosion resistance and casting flexibility are needed rather than high mechanical strength.

Common Applications of ADC1:
- Automotive Industry – Main frames, front panels, roof tiles
- Electrical Components – Charger lever for hybrid vehicle connectors
- Consumer Products – Inner pots for bread makers
- Building Materials – Escalator parts, roofing components
Example: Hybrid Vehicle Charging Connector Lever
ADC1 is used in charging connector levers for hybrid vehicles. These components are produced using a 40-ton vertical injection molding machine, followed by shot blasting and semi-gloss nickel chrome plating.
6. ADC1 vs. ADC12 Aluminum: What is the Difference & Which is Better?
ADC1 and ADC12 are both aluminum-silicon-based die casting alloys, but they have distinct differences in composition, strength, and applications.
| Property | ADC1 | ADC12 |
|---|---|---|
| Silicon (Si) Content | 11.0 – 13.0% | 9.6 – 12.0% |
| Copper (Cu) Content | ≤1.0% | 1.5 – 3.5% |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 290 | 320 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 130 | 160 |
| Elongation (%) | 3.5 | 1.0 |
| Hardness (HRB) | 38 | 45 |
| Castability | Excellent | Very good |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Machinability | Moderate | Good |
| Applications | Automotive frames, roofing materials, consumer electronics | Engine components, transmission cases, structural parts |
Which One is Better?
- ADC1 is preferred when corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and excellent castability are required. It is commonly used in automotive body structures, electrical components, and thin-walled cast parts.
- ADC12 offers higher strength and better machinability, making it ideal for engine parts, transmission housings, and other structural applications where mechanical performance is a priority.

