During the metal processing process, small edges or short strips of metal residue often appear on the cutting or cutting surface. This is what we often call “burrs”. The main reason for the formation of burrs is that during mechanical processing, there will inevitably be a certain amount of pressure between the cutting tool and the workpiece. These metal strips or granular residues may be left at the moment of metal delamination. If burrs cannot be removed in time, it will have a certain impact on subsequent processes or the use of products. Therefore, correct and effective burr removal is very important to ensure product quality. Commonly used deburring methods mainly include physical removal methods such as grinding, grinding, and polishing, as well as other methods such as chemical or electrolytic deburring. This article will introduce different deburring processes and their application scenarios to facilitate correct selection and application.
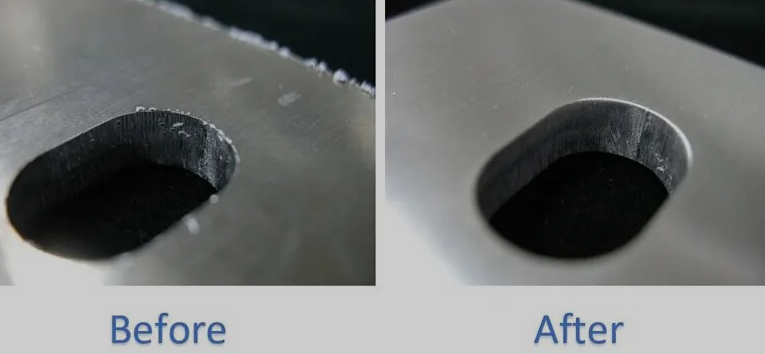
How do burrs affect metal processing?
Burrs can seriously affect the processing properties of metals:
- 1. Cause tool wear. The small tips of burrs can scratch tools, such as molds, cutting tools, etc., shortening the service life of tools.
- 2. Affect molding quality. Burrs will cause poor surface modeling of formed parts, making it impossible to meet the design dimensional accuracy requirements.
- 3. Cause product problems. Burrs may deviate from the forming position, affecting the installation and use of the product. Severe Deburring can cause product functionality to fail.
- 4. Formation of gap cracks. During the processing of metal, burrs may cause gaps and tiny cracks, affecting the strength and service life of the product.
- 5. Increase processing costs. In order to solve the burr problem, it is necessary to increase the deburring process, such as grinding, polishing, etc., thus increasing the cost.
- 6. Affect surface quality. Burrs will reduce the surface gloss and appearance quality of the product.
What are the causes of burrs during machining? How are burrs formed?
The main reasons for burrs during mechanical processing and the burr formation mechanism are as follows:
- -The cutting speed is too fast. Too high a cutting speed will cause instantaneous delamination on the metal surface, resulting in the formation of burrs on short metal wires.
- -The tool is too blunt and sharp. A dull tool will cause the metal to rub instead of cut, causing the metal to turn into short filaments.
- -The cutting temperature is too high. High temperatures will soften the metal surface, making it easier to delaminate and form burrs during cutting.
- -The material has uneven hardness. High local hardness will form fulcrums and produce longer burrs.
- -The cutting depth is too large. Cutting too deep at one time will cause high cutting stress and produce unnecessary burrs.
- -Tool wear. Severely worn tools will generate additional stress components, resulting in more burrs.
- -The machine transmission is not smooth. Insufficient power of the machine tool or transmission vibration will affect the cutting quality and form burrs.
The main machining processes that may leave burrs on metal surfaces include:
- -Milling processing: such as face milling, angle milling, etc.
- -Saw cutting processing
- – Boring processing
- -Drilling
- -Stamping and forming processing
- -Drawing processing
- -Grinding and polishing processing
The main cutting processes that can leave burrs on metal surfaces include:
- -Milling
- -saw cutting
- -Bore cutting
- -Drilling and cutting
How to remove burrs?
Next, let me introduce in detail the specific steps of physical deburring methods such as grinding, grinding and polishing:
- 1. Polishing method:
-Choose sandpaper with different thicknesses, such as 80, 120, 240, 400, etc.
-Place the parts to be removed on a stable base.
– Use sandpaper to manually rub and polish the working area from front, back, left, and right angles.
– Repeat the operation every time you change the level of sandpaper to see if the burrs are removed, otherwise continue to rub until the surface is smooth.
- 2. Grinding method:
-Choose an abrasive with appropriate rolling profile and thickness.
-Grind the part while holding it on the grinding wheel on the grinder.
-Select the grinding wheel speed and feeding rate according to the burr condition.
-Continuously grind and observe the surface to determine whether the burrs have been removed. Otherwise, replace the abrasive and continue grinding.
- 3. Polishing method:
-Based on sanding or grinding.
-Use a high-polymer polishing cloth or polishing fluid with a particle size of 0.5 μm.
-Multi-angle rhythmic polishing and extrusion friction are performed manually or mechanically.
-Continuously observe the surface brightness to determine whether careful polishing has been completed to remove gaps.
- 4. Electric drill processing: Use single electrode or multiple electrodes to remove burrs by drift sawing. The current strength and time control the removal degree.
- 5. Chemical hair removal: Use hair removal liquid to carry out chemical reaction to remove burrs. Choose a hair removal solution and soaking time suitable for the material and burr level.
- 6. Sliding grinding: Use the grinding wheel belt or the unique grinding structure of the belt to carry the sand to achieve grinding and hair removal.
- 7. Electrolytic hair removal: The electrolyte is applied to the metal surface to dissolve the electrolytic reaction ions to achieve hair removal.
- 8. Flame deburring: Use high-temperature flame to briefly and rapidly heat and ablate the burrs.

